RFID stands for Radio-Frequency Identification, which is a technology with many uses from automated checkout and return, asset tracking, theft prevention, animal identification, smart cards and defense supply chain automation. The technology is both simple and amazing, a tiny integrated circuit (chip) attached to foil antennas that transmits its identification number when interrogated by a radio signal. Read more about RFID Labeling for MS-129. ![]()
For the defense supply chain, these devices are generally embedded in thermal-transfer labels, similar to those on small parcels everywhere. However, the devices are practically unnoticeable unless one shines light through the label. They may also be used without a label, as what are referred to as inlays.
Passive RFID is just that. It just sits there passively until just the right radio signal hits it. The large antennas attached to the RFID chip collect up the energy from the radio signal allowing the chip enough energy to operate and transmit a radio signal with its identification number, sometimes referred to as a license plate. Because these chips do not require their own power, this elegantly simply design allows the devices to operate forever. There are also active RFID systems, which include batteries to allow them to constantly transmit. These are used in more specialized situations, such as defense cargo containers.
 How Does DoD Use RFID?
How Does DoD Use RFID?
The Department of Defense (DOD) and its associated agencies such as the Defense Logistics Agency (DLA) have many uses for RFID technology. The most significant is automation of receiving at DLA depots. Another is automation of disbursement personal items such as standard issue clothing and footwear items. Defense suppliers attach RF-tags to containers at two or three different packaging levels. The most prevalent use is the Case Label applied to an exterior container, which is defined by military standards (such as Mil-Std-129 and Mil-Std-2073) to be the container designed to protect items during shipment and storage. When RF-tagged Cases are put on a pallet a RFID Pallet Label is also attached to the pallet. RF-tagging at these two container levels allows the depots to process items without scanning barcode labels. Unit-level RFID tagging requirements are also found on defense contracts, however, their use is generally for disbursement rather than receiving. In the early days of RFID, it was thought that tagging everything would eliminate the need for checkers to assist shoppers with purchasing items. One would just load up their cart and get charged automatically as they left the store. There are some critical limitations to making that a reality, most due to the physics of radio waves and the physical properties of some items. However, the idea works very well with clothing items, so it is becoming more common for contracts to require Unit RFID tagging for such items to allow for the automation of disbursement of these items to our service members. |
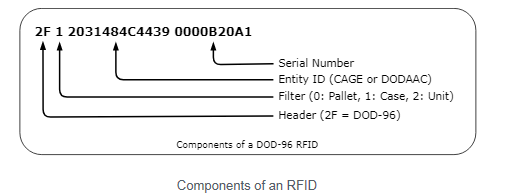
RFID automation seems like magic, but some very basic computing behind the scenes makes it all work. The ID transmitted by an RF-tag is referred to as a license plate because it does not communicate any information about the item or container it is attached to. It is simply twenty-four characters, that meet very specific requirements. For example, the tag 2F12031484C44390000B20A1 indicates that it is Case number 729249, issued by defense contractor 1HLD9. There is a bunch of data collection and computing behind the scenes that allows the depot to know that this box has a dozen canteens in it. It starts with the defense contractor submitting a Receiving Report (DD250) to Wide Area Workflow (WAWF) that included a list of the RFID Case tags in the shipment along with the number of each contact line item (CLIN) associated with each tag. When the case 2F12031484C44390000B20A1 arrives at the depot it goes through an RFID portal which interrogates the all the tags that are going by and looks them up in the information supplied by WAWF, and just like magic, knows that a dozen canteens were received on a specific defense contract shipment. Magic! |
It may seem redundant to put RF tags on both the Pallet and all of the Cases on it, however, there are reasons for both. When RFID data is provided to WAWF, in addition to the contents associated with each Case tag, the contractor lists the Cases on each Pallet tag. Ideally, when the Pallet tag is read by the depot it knows that each of the Cases has been received. This is important because sometimes stacked containers block or interfere with each other’s RF tags, particularly for small boxes in the middle. Individual Case tags on palletized shipments are also helpful if the pallet is broken apart, or when individual cases are later shipped to defense activities. The Case tags can also help the depot keep track of what it is loading for delivery to an activity. |
Just like barcodes and symbols, there is considerable variety in the types of technology used and the data stored and transmitted. For DOD use, a tag must be a 96-bit EPC UHF Gen 2 compatible, operating at 860-960MHz. While it would be possible to use other tags for this application, standardizing on one tag type allowed the DoD to minimize costs of deploying and interfacing readers. The DOD encoding standard defines how tag data is constructed by contractors and interpreted by depots. Take our example tag, it is composed of four parts:
At first glance, a nine-digit serial number may not seem to be enough to uniquely identify items forever. However, because it is a hexadecimal number, it can encode up to 68,719,476,736 unique tags. The Entity ID is also in hexadecimal, representing the ASCII codes for each character. The “2031484C4439” in the example is the CAGE code “1HLD9” in hexadecimal characters, with a leading space as a filler to allow for the use of six-digit DODAACs. |
Section 5.9 of Mil-Std-129R [5.9.1.a] Passive RFID tags shall be applied to case shipments and palletized unit load shipments. [5.9.2] A passive RFID tag may be integrated with the military or commercial shipping label (RFID-enabled address label) or it may be placed in a separate location on the shipment. [5.9.2.1.a.3] To preclude inventory and receipt issues associated with pallet-level data, the RFID-enabled tag attached to a palletized unit load should not be applied to an exterior container within the load. [5.9.2.1b] If RFID-enabled address labels are not used, then attach a separate passive RFID tag and a separate address label(s). [5.9.2.2] Exterior containers within a palletized unit load … will not usually be marked with an address label and therefore require only that the passive RFID tag be affixed at a suitable location where there is a minimum risk of damage and the highest potential for successful passive RFID tag interrogation. Paragraph 5.9.2.2 in particular differentiates between RF tags and RFID-enabled labels. This gives the contractor considerable flexibility in their implementation choices. This is important because while using an RFID-enabled Exterior Container or MSL label is generally the best option, the rules that control their placement can sometimes make them unreadable due to interaction between the tag antennas and the contents of the container. One particular example would be flat metal surfaces, like say a filing cabinet. Successful tagging of such an item might require what is known as a stand-off tag. Or the tag might need to be placed in over a void space in the container. In these cases, using an inlay or a generic RFID label would be the best choice. |